AMAZON RDS CUSTOM
Amazon RDS Custom is a managed database service for applications that require customization of the underlying operating system and database environment. Benefits of RDS automation with the access needed for legacy, packaged, and custom applications.
Addressing the challenge of database customization
Amazon RDS Custom brings the benefits of Amazon RDS to a market that can't easily move to a fully managed service because of customizations that are required with third-party applications. Amazon RDS Custom saves administrative time, is durable, and scales with your business.
If you need the entire database and operating system to be fully managed by AWS, we recommend Amazon RDS. If you need administrative rights to the database and underlying operating system to make dependent applications available, Amazon RDS Custom is the better choice. If you want full management responsibility and simply need a managed compute service, the best option is self-managing your commercial databases on Amazon EC2.
To deliver a managed service experience, Amazon RDS doesn't let you access the underlying host. Amazon RDS also restricts access to some procedures and objects that require high-level privileges. However, for some applications, you might need to perform operations as a privileged operating system (OS) user.
For example, you might need to do the following:
Install custom database and OS patches and packages.
Configure specific database settings.
Configure file systems to share files directly with their applications.
Previously, if you needed to customize your application, you had to deploy your database on-premises or on Amazon EC2. In this case, you bear most or all of the responsibility for database management, as summarized in the following table.
Feature | On-premises responsibility | Amazon EC2 responsibility | Amazon RDS responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
Application optimization | Customer | Customer | Customer |
Scaling | Customer | Customer | AWS |
High availability | Customer | Customer | AWS |
Database backups | Customer | Customer | AWS |
Database software patching | Customer | Customer | AWS |
Database software install | Customer | Customer | AWS |
OS patching | Customer | Customer | AWS |
OS installation | Customer | Customer | AWS |
Server maintenance | Customer | AWS | AWS |
Hardware lifecycle | Customer | AWS | AWS |
Power, network, and cooling | Customer | AWS | AWS |
When you manage database software yourself, you gain more control, but you're also more prone to user errors. For example, when you make changes manually, you might accidentally cause application downtime. You might spend hours checking every change to identify and fix an issue. Ideally, you want a managed database service that automates common DBA tasks, but also supports privileged access to the database and underlying operating system.
Management model and benefits for Amazon RDS Custom
Amazon RDS Custom is a managed database service for legacy, custom, and packaged applications that require access to the underlying operating system and database environment. Amazon RDS Custom automates setup, operation, and scaling of databases in the AWS Cloud while granting you access to the database and underlying operating system. With this access, you can configure settings, install patches, and enable native features to meet the dependent application's requirements. With RDS Custom, you can run your database workload using the AWS Management Console or the AWS CLI.
Currently, Amazon RDS Custom supports only the Oracle Database and Microsoft SQL Server engines.
Shared responsibility model
With Amazon RDS Custom, you get the automation of Amazon RDS and the flexibility of Amazon EC2. You take on on additional database management responsibilities beyond what you do in Amazon RDS. By doing so, you can benefit from RDS automation and the deeper customization of EC2. To meet your application and business requirements, you manage the host yourself.
In the shared responsibility model of RDS Custom, you get more control than in Amazon RDS but also more responsibility. Shared responsibility has two meanings:
You own part of the process when using a feature.
You have full access to the feature, and it's your responsibility to make sure that any customizations work with that feature.
The following table details the shared responsibility model for RDS Custom.
Feature | Amazon EC2 responsibility | Amazon RDS responsibility | RDS Custom for Oracle responsibility | RDS Custom for SQL Server responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Application optimization | Customer | Customer | Customer | Customer |
Scaling | Customer | AWS | Shared | Shared |
High availability | Customer | AWS | Customer | Customer |
Database backups | Customer | AWS | Shared | Shared |
Database software patching | Customer | AWS | Shared | AWS |
Database software install | Customer | AWS | Shared | AWS |
OS patching | Customer | AWS | Customer | AWS |
OS installation | Customer | AWS | Shared | AWS |
Server maintenance | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS |
Hardware lifecycle | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS |
Power, network, and cooling | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS |
You can create an RDS Custom DB instance using Microsoft SQL Server. In this case:
You don't manage your own media.
You don't need to purchase SQL Server licenses separately. AWS holds the license for the SQL Server database software.
You can create an RDS Custom DB instance using Oracle Database. In this case, you do the following:
Manage your own media.
When using RDS Custom, you upload your own database installation files and patches. You create a custom engine version (CEV) from these files. Then you can create an RDS Custom DB instance by using this CEV.
Manage your own licenses.
You bring your own Oracle Database licenses and manage licenses by yourself.
Key benefits of RDS Custom
With RDS Custom, you can do the following:
Automate many of the same administrative tasks as Amazon RDS, including the following:
Lifecycle management of databases
Automated backups and point-in-time recovery (PITR)
Monitoring the health of RDS Custom DB instances and observing changes to the infrastructure, operating system, and databases
Notification or taking action to fix issues depending on disruption to the DB instance
Install third-party applications.
You can install software to run custom applications and agents. Because you have privileged access to the host, you can modify file systems to support legacy applications.
Install custom patches.
You can apply custom database patches or modify OS packages on your RDS Custom DB instances.
Stage an on-premises database before moving it to a fully managed service.
If you manage your own on-premises database, you can stage the database to RDS Custom as-is. After you familiarize yourself with the cloud environment, you can migrate your database to a fully managed Amazon RDS DB instance.
Create your own automation.
You can create, schedule, and run custom automation scripts for reporting, management, or diagnostic tools.
Amazon RDS Custom architecture
VPC
As in Amazon RDS, your RDS Custom DB instance resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC).
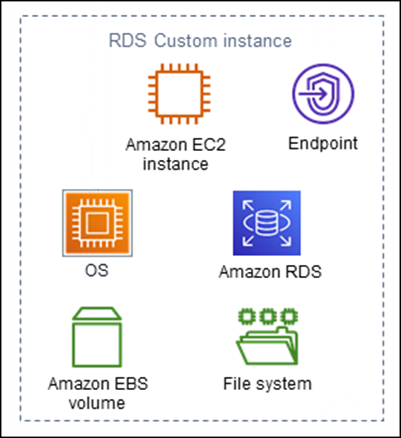
The DB instance consists of the following main components:
Amazon EC2 instance
Instance endpoint
Operating system installed on the Amazon EC2 instance
Amazon EBS storage, which contains any additional file systems
Amazon S3
If you use RDS Custom for Oracle, you upload installation media to a user-created Amazon S3 bucket. RDS Custom for Oracle uses the media in this bucket to create a custom engine version (CEV). A CEV is a binary volume snapshot of a database version and Amazon Machine Image (AMI). From the CEV, you can create an RDS Custom DB instance. AWS CloudTrail logs for the trail created by RDS Custom
Database redo log files (RDS Custom for Oracle only)
Transaction logs (RDS Custom for SQL Server only)
Custom engine version artifacts (RDS Custom for Oracle only)
RDS Custom creates the do-not-delete-rds-custom- S3 bucket when you create either of the following resources:
Your first CEV for RDS Custom for Oracle
Your first DB instance for RDS Custom for SQL Server
RDS Custom creates one bucket for each combination of the following:
AWS account ID
Engine type (either RDS Custom for Oracle or RDS Custom for SQL Server)
AWS Region
For example, if you create RDS Custom for Oracle CEVs in a single AWS Region, one do-not-delete-rds-custom- bucket exists. If you create multiple RDS Custom for SQL Server instances, and they reside in different AWS Regions, one do-not-delete-rds-custom- bucket exists in each AWS Region. If you create one RDS Custom for Oracle instance and two RDS Custom for SQL Server instances in a single AWS Region, two do-not-delete-rds-custom- buckets exist.
AWS CloudTrail
RDS Custom automatically creates an AWS CloudTrail trail whose name begins with do-not-delete-rds-custom-. The RDS Custom support perimeter relies on the events from CloudTrail to determine whether your actions affect RDS Custom automation. For more information, see Support perimeter.
RDS Custom creates the trail when you create your first DB instance. RDS Custom creates one trail for each combination of the following:
AWS account ID
Engine type (either RDS Custom for Oracle or RDS Custom for SQL Server)
AWS Region
RDS Custom automation and monitoring
RDS Custom has automation software that runs outside of the DB instance. This software communicates with agents on the DB instance and with other components within the overall RDS Custom environment.
Monitoring and recovery
The RDS Custom monitoring and recovery features offer similar functionality to Amazon RDS. By default, RDS Custom is in full automation mode. The automation software has the following primary responsibilities:
Collect metrics and send notifications
Perform automatic instance recovery
An important responsibility of RDS Custom automation is responding to problems with your Amazon EC2 instance. For various reasons, the host might become impaired or unreachable. RDS Custom resolves these problems by either rebooting or replacing the Amazon EC2 instance.



Amazon SNS makes it simple and cost effective to send push notifications to mobile device users, email recipients or even send messages to other distributed services.
𝗙𝗲𝗮𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗔𝗺𝗮𝘇𝗼𝗻 𝗦𝗡𝗦
Automatic Scaling
Message Encryption
Message Filtering
Message Fanout
Mobile Notification
SNS & Email Messages